Big Data Technology
What is Hadoop? What is MapReduce? What is NoSQL?

The flow rate of data in this modern age – think of the Hoover Dam flooding the Colorado river
As the world becomes more information-driven than ever before, a major challenge has become how to deal with the explosion of data. Traditional frameworks of data management now buckle under the gargantuan volume of today's datasets. Fortunately, a rapidly changing landscape of new technologies is redefining how we work with data at super-massive scale. These technologies demand a new breed of DBAs and infrastructure engineers/developers to manage far more sophisticated systems.
Here is an overview of important technologies to know about for context around big data infrastructure.
- Traditional RDBMS (older technology, losing relevance)
- NoSQL Database Systems
- Hadoop, MapReduce, and massively parallel computing
What is a Relational Database?
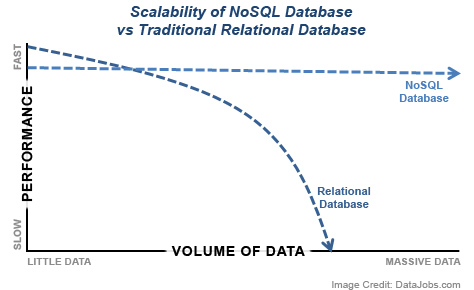
Traditional RDBMS (relational database management system) have been the de facto standard for database management throughout the age of the internet. The architecture behind RDBMS is such that data is organized in a highly-structured manner, following the relational model. Though, RDBMS is now considered to be a declining database technology. While the precise organization of the data keeps the warehouse very "neat", the need for the data to be well-structured actually becomes a substantial burden at extremely large volumes, resulting in performance declines as size gets bigger. Thus, RDBMS is generally not thought of as a scalable solution to meet the needs of 'big' data.
What is NoSQL?
NoSQL (commonly referred to as "Not Only SQL") represents a completely different framework of databases that allows for high-performance, agile processing of information at massive scale. In other words, it is a database infrastructure that as been very well-adapted to the heavy demands of big data.
The efficiency of NoSQL can be achieved because unlike relational databases that are highly structured, NoSQL databases are unstructured in nature, trading off stringent consistency requirements for speed and agility. NoSQL centers around the concept of distributed databases, where unstructured data may be stored across multiple processing nodes, and often across multiple servers. This distributed architecture allows NoSQL databases to be horizontally scalable; as data continues to explode, just add more hardware to keep up, with no slowdown in performance. The NoSQL distributed database infrastructure has been the solution to handling some of the biggest data warehouses on the planet – i.e. the likes of Google, Amazon, and the CIA.
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is not a type of database, but rather a software ecosystem that allows for massively parallel computing. It is an enabler of certain types NoSQL distributed databases (such as HBase), which can allow for data to be spread across thousands of servers with little reduction in performance.
A staple of the Hadoop ecosystem is MapReduce, a computational model that basically takes intensive data processes and spreads the computation across a potentially endless number of servers (generally referred to as a Hadoop cluster). It has been a game-changer in supporting the enormous processing needs of big data; a large data procedure which might take 20 hours of processing time on a centralized relational database system, may only take 3 minutes when distributed across a large Hadoop cluster of commodity servers, all processing in parallel.
The Bottom Line
As big data continues down its path of growth, there is no doubt that these innovative approaches – utilizing NoSQL database architecture and Hadoop software – will be central to allowing companies reach full potential with data. Additionally, this rapid advancement of data technology has sparked a rising demand to hire the next generation of technical geniuses who can build up this powerful infrastructure. The cost of the technology and the talent may not be cheap, but for all of the value that big data is capable of bringing to table, companies are finding that it is a very worthy investment.

